A physical event, phenomenon or activity that has the potentially to cause the loss of life or injury, property damage, social and economic disruption or environmental degradation e.g. earthquake, flood, drought, tsunami, cyclone etc. Each hazard is characterized by its location, intensity, frequency and probability.
Classification of Hazards
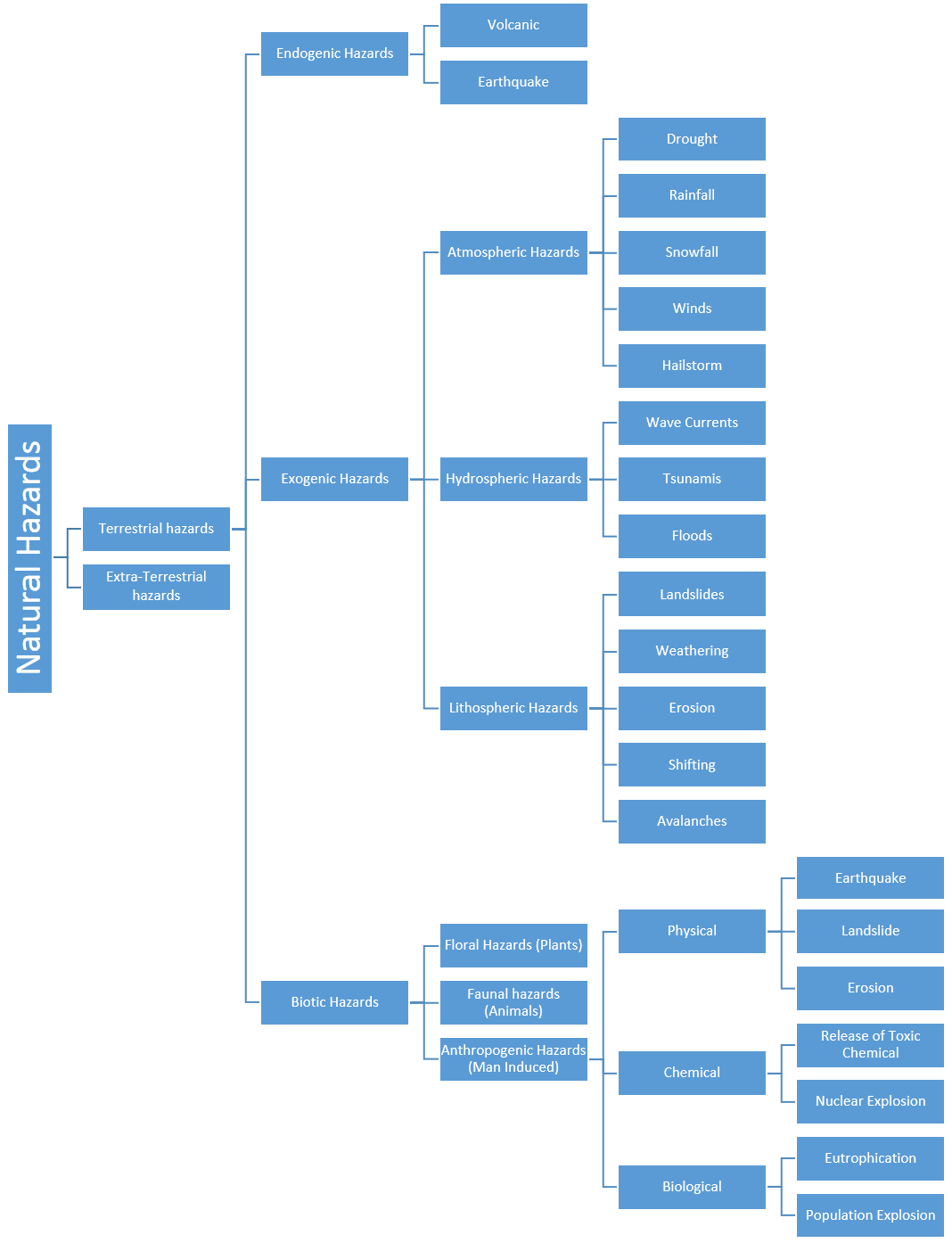
On the basis of origin of the hazards:
-
Natural Hazards
-
Terrestrial hazards
-
Endogenic Hazards
- Volcanic
- Earthquake
-
Exogenic Hazards
- Atmospheric Hazards
- Drought
- Rainfall
- Snowfall
- Winds
- Hailstorm
-
Hydrospheric Hazards
- Wave Currents
- Tsunamis
- Floods
-
Lithospheric Hazards
- Landslides
- Weathering
- Erosion
- Shifting
- Avalanches
- Biotic Hazards
- Floral Hazards (Plants)
- Faunal hazards (Animals)
-
Anthropogenic Hazards (Man Induced)
- Physical
- Earthquake
- Landslide
- Erosion
- Chemical
- Release of Toxic Chemical
- Nuclear Explosion
-
Biological
- Eutrophication
- Population Explosion
-
Endogenic Hazards
- Extra-Terrestrial hazards
-
Terrestrial hazards
1. Natural Hazards
a. Terrestrial hazards
Those hazards which originate inside the earth or its atmosphere are called terrestrial hazards.
i. Endo-genic Hazards
Hazards which originate inside the surface of the earth are termed as endogenic hazards. E.g. Volcanic, Earthquake
ii. Exo-genic Hazards
Hazards which originate above the surface of the earth (in the atmosphere) are called exogenic hazards. These can be further sub-divided into the following categories:
A. Atmospheric Hazards
Natural hazards that originate in the atmosphere of the earth are called atmospheric hazards. These include cyclones, tornadoes, droughts, thunderstorms etc. Drought, Rainfall, Snowfall, Winds, Hailstorm
B. Hydrospheric Hazards
Those natural hazards that are related to water in the atmosphere are termed as hydrospheric hazards. Wave Currents, Tsunamis, Floods
C. Lithospheric Hazards
Lithospheric hazards are those natural hazards that occur near to the surface of the earth. It includes the following hazards: Landslides, weathering, erosion, shifting, avalanches, sink Holes
Calcium carbonate inside the surface of the earth is dissolved by the underground running water and taken away with it, creating holes. This causes the earth to become hollow and eventually the earth above it settles down under load.
iii. Biotic Hazards
The types of hazards that originate through plants, animals or humans.
A. Floral Hazards (Plants)
The type of hazards that originate from plant life.
B. Faunal hazards (Animals)
C. Anthropogenic Hazards (Man Induced)
1. Physical
Earthquake, Landslide, Erosion
2. Chemical
Release of Toxic Chemical, Nuclear Explosion
3. Biological
Eutrophication, Population Explosion
b. Extra-Terrestrial hazards
The kinds of hazards which originate outside the earth and its atmosphere are called extra-terrestrial hazards. e.g meteorites.
Category:
